34 分钟
单元测试框架
学习如何使用 Matchstick,一个由 [LimeChain]开发的单元测试框架(https://limechain.tech/)。 Matchstick使子图开发者能够在沙盒环境中测试其绘图逻辑并成功地部署其子图。
使用Matchstick的好处
- 它用Rust编写并优化高性能。
- 它允许您访问开发者功能,包括模拟合约通话的能力 对商店状态进行断言、监视子图失败、检查测试性能等等。
开始
安装依赖项
为了使用测试辅助器方法并运行测试,您需要安装以下依赖项:
1yarn add --dev matchstick-as安装PostgreSQL
graph-node依赖于PostgreSQL,所以如果你还没有它,你将需要安装它。
注意:强烈建议使用下面的命令来避免意外错误。
使用 MacOS
安装命令:
1酿造安装postgresql创建到最新 libpq.5. lib 的符号链接,可能需要首先创建这个目录/usr/local/opt/postgreql/lib/`
1ln -sf /usr/local/opt/postgresql@14/lib/postgresql@14/libpq.5.dylib /usr/local/opt/postgresql/lib/libpq.5.dylib使用 Linux
安装命令(取决于您的拆分):
1sudo apt install postgresql使用 WSL (window子系统为 Linux)
可以使用 Docker 方法和二进制方法在 WSL 上使用 Matchstick。由于 WSL 可能有点复杂,所以这里有一些提示,以防您遇到诸如
1static BYTES = Symbol("Bytes") SyntaxError: Unexpected token =或者
1<PROJECT_PATH>/node_modules/gluegun/build/index.js:13 throw up;请确保您是新版本的 Node.js graph-cli 不支持 v10.19.0 ,这仍然是WSL上新的 Ubuntu 图像的默认版本。 例如,Matchstick被确认在 WSL 使用 **v18.1.0 **,您可以通过 nvm 切换到它,也可以更新您的全局Node.js。 别忘了在更新节点后删除 node_modules 并重新运行 npm install ! 然后,请确保您已经安装了 libpq ,您可以通过运行来做到这一点。
1sudo apt-get install libpq-dev最后, 不要使用 graph test (它使用您的全局安装图形-cli ,并且出于某些原因看起来像当前WSL 上的故障), 相反,使用 yarn test 或 npm 运行测试 (这将使用当地、项目一级的graph-cli 实例,它类似于一个字符)。 因此,你当然需要在你的package.json 文件中有一个 “test"" 脚本,这个脚本可以像这样简单。
1{2 "name": "demo-subgraph",3 "version": "0.1.0",4 "scripts": {5 "test": "graph test",6 ...7 },8 "dependencies": {9 "@graphprotocol/graph-cli": "^0.56.0",10 "@graphprotocol/graph-ts": "^0.31.0",11 "matchstick-as": "^0.6.0"12 }13}使用 Matchstick
要在子图项目中使用Matchstick,只需打开一个终端,导航到项目的根文件夹,然后简单地运行graph test [options] <datasource>-它下载最新的Matchstick二进制文件,并在测试文件夹中运行指定的测试或所有测试(如果未指定数据源标志,则运行所有现有测试)。
CLI 选项
这将运行测试文件夹中的所有测试:
1graph test这将运行名为gravity.test.ts的测试和/或名为gravity的文件夹中的所有测试:
1graph test Gravity这将仅运行特定的测试文件:
1graph test path/to/file.test.ts选项:
1-c, --coverage Run the tests in coverage mode2-d, --docker Run the tests in a docker container (Note: Please execute from the root folder of the Subgraph)3-f, --force Binary: Redownloads the binary. Docker: Redownloads the Dockerfile and rebuilds the docker image.4-h, --help Show usage information5-l, --logs Logs to the console information about the OS, CPU model and download url (debugging purposes)6-r, --recompile Forces tests to be recompiled7-v, --version <tag> Choose the version of the rust binary that you want to be downloaded/usedDocker
从 graph-cli 0.25.2, graph test 命令支持使用 -d 标志在一个码头容器中运行 matchstick 。 停泊器实现使用 绑定挂载,所以它不必在执行”Graph test -d” 命令时重建停泊器图像。 你也可以按照 matchstick的指令手动运行停靠仓库。
❗ graph test -d 强制docker run 使用标志-t运行。这必须移除以在非交互环境中运行(如GitHub CI)。
❗ 如果你以前运行过graph test, 在docker构建过程中可能会遇到以下错误:
1error from sender: failed to xattr node_modules/binary-install-raw/bin/binary-<platform>: permission denied在这种情况下,在根文件夹中创建 .dockerignore 并添加 node_modules/biny-install-raw/bin。
配置
Matchstick可以通过matchstick.yaml配置文件配置为使用自定义测试、库和清单路径:
1testsFolder: path/to/tests2libsFolder: path/to/libs3manifestPath: path/to/subgraph.yaml演示子图
你可以尝试通过克隆Demo Subgraph repo 来使用本指南的示例。
视频教程
此外,您还可以查看“如何使用Matchstick为子图编写单元测试”系列视频。
测试结构
IMPORTANT:下面描述的测试结构取决于matchstick-as版本 >=0.5.0
描述()
description(name: String , () => {}) - 定义测试组。
注意:
- 描述不是强制性的。您仍然可以在describe()区块之外,以旧的方式使用test()
例子:
1import { describe, test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar()", () => {5 test("Should create a new Gravatar entity", () => {6 ...7 })8})嵌套的 descrip() 示例:
1import { describe, test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleUpdatedGravatar()", () => {5 describe("When entity exists", () => {6 test("updates the entity", () => {7 ...8 })9 })1011 describe("When entity does not exists", () => {12 test("it creates a new entity", () => {13 ...14 })15 })16})测试()
test(name: String, () =>, should_fail: bool) - 定义测试案例。您可以在描述() 块内或独立使用test()。
例子:
1import { describe, test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar()", () => {5 test("Should create a new Entity", () => {6 ...7 })8})或者
1test("handleNewGravatar() should create a new entity", () => {2 ...3})beforeAll()
在文件中的任何测试之前运行代码区块。如果beforeAll在describe区块内声明,它将在该describe区块的开头运行。
例子:
beforeAll中的代码将在第一个描述区块中的所有测试之前执行一次。
1import { describe, test, beforeAll } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"3import { Gravatar } from "../../generated/schema"45beforeAll(() => {6 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")7 gravatar.displayName = “First Gravatar”8 gravatar.save()9 ...10})1112describe("When the entity does not exist", () => {13 test("it should create a new Gravatar with id 0x1", () => {14 ...15 })16})1718describe("When entity already exists", () => {19 test("it should update the Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {20 ...21 })22})beforeAll中的代码将在第一个描述区块中的所有测试之前执行一次。
1import { describe, test, beforeAll } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"3import { Gravatar } from "../../generated/schema"45describe("handleUpdatedGravatar()", () => {6 beforeAll(() => {7 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")8 gravatar.displayName = “First Gravatar”9 gravatar.save()10 ...11 })1213 test("updates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {14 ...15 })1617 test("creates new Gravatar with id 0x1", () => {18 ...19 })20})afterAll()
在每次测试后运行代码区块。如果afterAll在describe 区块中声明,则在该describe 区块中的每个测试之后运行。
例子:
afterAll中的代码将在第一个描述区块中的所有测试之后执行一次。
1import { describe, test, afterAll } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"3import { store } from "@graphprotocol/graph-ts"45afterAll(() => {6 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x0")7 ...8})910describe("handleNewGravatar, () => {11 test("creates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {12 ...13 })14})1516describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {17 test("updates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {18 ...19 })20})afterAll中的代码将在第一个描述区块中的所有测试之后执行一次。
1import { describe, test, afterAll, clearStore } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar", () => {5 afterAll(() => {6 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x1")7 ...8 })910 test("It creates a new entity with Id 0x0", () => {11 ...12 })1314 test("It creates a new entity with Id 0x1", () => {15 ...16 })17})1819describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {20 test("updates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {21 ...22 })23})beforeEach()
在文件中的任何测试之前运行代码区块。如果beforeEach在describe区块内声明,它将在该describe区块的每次测试之前运行。
示例:在每次测试之前,beforeEach中的代码将会执行。
1import { describe, test, beforeEach, clearStore } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleNewGravatars } from "./utils"34beforeEach(() => {5 clearStore() // <-- clear the store before each test in the file6})78describe("handleNewGravatars, () => {9 test("A test that requires a clean store", () => {10 ...11 })1213 test("Second that requires a clean store", () => {14 ...15 })16})1718 ...beforeEach 里的代码将仅在描述中的每个测试之前执行。
1import { describe, test, beforeEach } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from '../../src/gravity'34describe('handleUpdatedGravatars', () => {5 beforeEach(() => {6 let gravatar = new Gravatar('0x0')7 gravatar.displayName = 'First Gravatar'8 gravatar.imageUrl = ''9 gravatar.save()10 })1112 test('Updates the displayName', () => {13 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'displayName', 'First Gravatar')1415 // code that should update the displayName to 1st Gravatar1617 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'displayName', '1st Gravatar')18 store.remove('Gravatar', '0x0')19 })2021 test('Updates the imageUrl', () => {22 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'imageUrl', '')2324 // code that should changes the imageUrl to https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x02526 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'imageUrl', 'https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x0')27 store.remove('Gravatar', '0x0')28 })29})afterEach()
在文件中的任何测试之前运行代码区块。如果beforeEach在describe区块内声明,它将在该describe区块的每次测试之前运行。
例子:
AfterEach中的代码将仅在描述中的每个测试之后执行。
1import { describe, test, beforeEach, afterEach } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34beforeEach(() => {5 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")6 gravatar.displayName = “First Gravatar”7 gravatar.save()8})910afterEach(() => {11 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x0")12})1314describe("handleNewGravatar", () => {15 ...16})1718describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {19 test("Updates the displayName", () => {20 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "First Gravatar")2122 // code that should update the displayName to 1st Gravatar2324 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "1st Gravatar")25 })2627 test("Updates the imageUrl", () => {28 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "")2930 // code that should changes the imageUrl to https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x03132 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x0")33 })34})AfterEach中的代码将仅在描述中的每个测试之后执行。
1import { describe, test, beforeEach, afterEach } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar", () => {5 ...6})78describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {9 beforeEach(() => {10 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")11 gravatar.displayName = "First Gravatar"12 gravatar.imageUrl = ""13 gravatar.save()14 })1516 afterEach(() => {17 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x0")18 })1920 test("Updates the displayName", () => {21 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "First Gravatar")2223 // code that should update the displayName to 1st Gravatar2425 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "1st Gravatar")26 })2728 test("Updates the imageUrl", () => {29 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "")3031 // code that should changes the imageUrl to https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x03233 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x0")34 })35})判断
1fieldEquals(entityType: string, id: string, fieldName: string, expectedVal: string)23equals(expected: ethereum.Value, actual: ethereum.Value)45notInStore(entityType: string, id: string)67addressEquals(address1: Address, address2: Address)89bytesEquals(bytes1: Bytes, bytes2: Bytes)1011i32Equals(number1: i32, number2: i32)1213bigIntEquals(bigInt1: BigInt, bigInt2: BigInt)1415booleanEquals(bool1: boolean, bool2: boolean)1617stringEquals(string1: string, string2: string)1819arrayEquals(array1: Array<ethereum.Value>, array2: Array<ethereum.Value>)2021tupleEquals(tuple1: ethereum.Tuple, tuple2: ethereum.Tuple)2223assertTrue(value: boolean)2425assertNull<T>(value: T)2627assertNotNull<T>(value: T)2829entityCount(entityType: string, expectedCount: i32)截至版本 0.6.0,我们也支持自定义错误消息。
1assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x123', 'id', '0x123', 'Id should be 0x123')2assert.equals(ethereum.Value.fromI32(1), ethereum.Value.fromI32(1), 'Value should equal 1')3assert.notInStore('Gravatar', '0x124', 'Gravatar should not be in store')4assert.addressEquals(Address.zero(), Address.zero(), 'Address should be zero')5assert.bytesEquals(Bytes.fromUTF8('0x123'), Bytes.fromUTF8('0x123'), 'Bytes should be equal')6assert.i32Equals(2, 2, 'I32 should equal 2')7assert.bigIntEquals(BigInt.fromI32(1), BigInt.fromI32(1), 'BigInt should equal 1')8assert.booleanEquals(true, true, 'Boolean should be true')9assert.stringEquals('1', '1', 'String should equal 1')10assert.arrayEquals([ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)], [ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)], 'Arrays should be equal')11assert.tupleEquals(12 changetype<ethereum.Tuple>([ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)]),13 changetype<ethereum.Tuple>([ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)]),14 'Tuples should be equal',15)16assert.assertTrue(true, 'Should be true')17assert.assertNull(null, 'Should be null')18assert.assertNotNull('not null', 'Should be not null')19assert.entityCount('Gravatar', 1, 'There should be 2 gravatars')20assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 1, 'GraphTokenLockWallet template should have one data source')21assert.dataSourceExists(22 'GraphTokenLockWallet',23 Address.zero().toHexString(),24 'GraphTokenLockWallet should have a data source for zero address',25)编写一个单元测试
让我们看看一个简单的单元测试,如何看起来像在 Demo Subgraph中使用 Gravatar 示例。
假设我们有以下处理程序函数(以及两个帮助函数,以使我们的生活更轻松):
1export function handleNewGravatar(event: NewGravatar): void {2 let gravatar = new Gravatar(event.params.id.toHex())3 gravatar.owner = event.params.owner4 gravatar.displayName = event.params.displayName5 gravatar.imageUrl = event.params.imageUrl6 gravatar.save()7}89export function handleNewGravatars(events: NewGravatar[]): void {10 events.forEach((event) => {11 handleNewGravatar(event)12 })13}1415export function createNewGravatarEvent(16 id: i32,17 ownerAddress: string,18 displayName: string,19 imageUrl: string,20): NewGravatar {21 let mockEvent = newMockEvent()22 let newGravatarEvent = new NewGravatar(23 mockEvent.address,24 mockEvent.logIndex,25 mockEvent.transactionLogIndex,26 mockEvent.logType,27 mockEvent.block,28 mockEvent.transaction,29 mockEvent.parameters,30 )31 newGravatarEvent.parameters = new Array()32 let idParam = new ethereum.EventParam('id', ethereum.Value.fromI32(id))33 let addressParam = new ethereum.EventParam(34 'ownerAddress',35 ethereum.Value.fromAddress(Address.fromString(ownerAddress)),36 )37 let displayNameParam = new ethereum.EventParam('displayName', ethereum.Value.fromString(displayName))38 let imageUrlParam = new ethereum.EventParam('imageUrl', ethereum.Value.fromString(imageUrl))3940 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(idParam)41 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(addressParam)42 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(displayNameParam)43 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(imageUrlParam)4445 return newGravatarEvent46}我们首先必须在项目中创建一个测试文件。这是一个示例,说明它可能是什么样子的:
1import { clearStore, test, assert } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { Gravatar } from '../../generated/schema'3import { NewGravatar } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'4import { createNewGravatarEvent, handleNewGravatars } from '../mappings/gravity'56test('Can call mappings with custom events', () => {7 // Create a test entity and save it in the store as initial state (optional)8 let gravatar = new Gravatar('gravatarId0')9 gravatar.save()1011 // Create mock events12 let newGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(12345, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')13 let anotherGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(3546, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')1415 // Call mapping functions passing the events we just created16 handleNewGravatars([newGravatarEvent, anotherGravatarEvent])1718 // Assert the state of the store19 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', 'gravatarId0', 'id', 'gravatarId0')20 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '12345', 'owner', '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7')21 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '3546', 'displayName', 'cap')2223 // Clear the store in order to start the next test off on a clean slate24 clearStore()25})2627test('Next test', () => {28 //...29})还有很多东西可以解包! 首先,我们注意到的一个重要问题是,我们正在从 matchstick-as、我们的 AssemblyScript 助手库中导入一些东西(作为npm 模块分发)。 您可以在这里找到仓库。 matchstick-as为我们提供了有用的测试方法,并定义了test()功能,我们将用它来构建我们的测试块。 其它部分相当直截了当――这里发生了什么事:
- 我们正在设置我们的初始状态并添加一个自定义的 Gravatar 实体。
- 我们使用
createNewGravatarEvent()函数定义两个NewGravatar事件对象及其数据; - 我们正在调用这些事件的处理方法 -
handleNewGravatars()并在我们的自定义事件列表中传递; - 我们断定存储的状态。那是怎么实现的呢?- 我们传递一个实体类型和 id 的唯一组合。然后我们检查该实体的一个特定字段,并断定它具有我们期望的值。我们为我们添加到存储的初始 Gravatar 实体,以及当处理函数被调用时被添加的两个 Gravatar 实体都做这个。
- 最后——我们正在使用
clearStore()来清理内存,以便我们的下一次测试能够以一个新的和空的储存对象开始。 我们可以定义我们想要的尽可能多的试验区块。
好了,我们创建了第一个测试!👏
现在,为了运行我们的测试,您只需在子图根文件夹中运行以下命令:
graph test Gravity
如果一切顺利,您应该会收到以下信息:
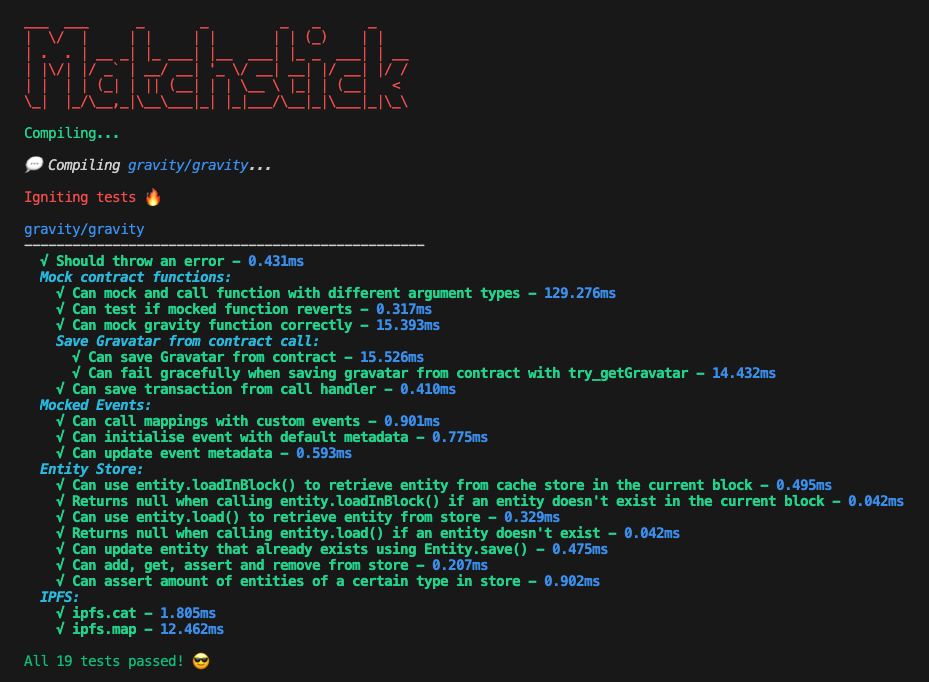
常见测试场景
使用特定状态来填充存储
用户能够用一组已知的实体来补充存储。下面是一个用Gravatar实体初始化存储的例子。
1let gravatar = new Gravatar('entryId')2gravatar.save()用一个事件调用一个映射函数
用户可以创建自定义事件并将其传递给绑定到存储的映射函数:
1import { store } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'2import { NewGravatar } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'3import { handleNewGravatars, createNewGravatarEvent } from './mapping'45let newGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(12345, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')67handleNewGravatar(newGravatarEvent)用事件夹具调用所有的映射关系
用户可以用测试夹具调用所有的映射关系。
1import { NewGravatar } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'2import { store } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'3import { handleNewGravatars, createNewGravatarEvent } from './mapping'45let newGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(12345, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')67let anotherGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(3546, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')89handleNewGravatars([newGravatarEvent, anotherGravatarEvent])1export function handleNewGravatars(events: NewGravatar[]): void {2 events.forEach(event => {3 handleNewGravatar(event);4 });5}模拟合约调用
用户可以模拟合约调用:
1import { addMetadata, assert, createMockedFunction, clearStore, test } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { Gravity } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'3import { Address, BigInt, ethereum } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'45let contractAddress = Address.fromString('0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7')6let expectedResult = Address.fromString('0x90cBa2Bbb19ecc291A12066Fd8329D65FA1f1947')7let bigIntParam = BigInt.fromString('1234')8createMockedFunction(contractAddress, 'gravatarToOwner', 'gravatarToOwner(uint256):(address)')9 .withArgs([ethereum.Value.fromSignedBigInt(bigIntParam)])10 .returns([ethereum.Value.fromAddress(Address.fromString('0x90cBa2Bbb19ecc291A12066Fd8329D65FA1f1947'))])1112let gravity = Gravity.bind(contractAddress)13let result = gravity.gravatarToOwner(bigIntParam)1415assert.equals(ethereum.Value.fromAddress(expectedResult), ethereum.Value.fromAddress(result))如图所示,为了模拟合约调用并实现返回值,用户必须提供合约地址、函数名、函数签名、参数数组,当然还有返回值。
用户还可以模拟函数还原:
1let contractAddress = Address.fromString('0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7')2createMockedFunction(contractAddress, 'getGravatar', 'getGravatar(address):(string,string)')3 .withArgs([ethereum.Value.fromAddress(contractAddress)])4 .reverts()模拟IPFS文件(from matchstick 0.4.1)
用户可以使用 mockIpfsFile(hash, filePath) 函数模拟IPFS 文件。 函数接受两个参数,第一个参数是IPFS 文件哈希/路径,第二个参数是本地文件的路径。
注意:在测试ipfs.map/ipfs.mapJSON,时,必须从测试文件中导出回调函数,以便matchstck检测到它,如下面测试示例中的processGravatar() 函数:
.test.ts file:
1import { assert, test, mockIpfsFile } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { ipfs } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'3import { gravatarFromIpfs } from './utils'45// Export ipfs.map() callback in order for matchstick to detect it6export { processGravatar } from './utils'78test('ipfs.cat', () => {9 mockIpfsFile('ipfsCatfileHash', 'tests/ipfs/cat.json')1011 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 0)1213 gravatarFromIpfs()1415 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 1)16 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '1', 'imageUrl', 'https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MELP46s8Cic/maxresdefault.jpg')1718 clearStore()19})2021test('ipfs.map', () => {22 mockIpfsFile('ipfsMapfileHash', 'tests/ipfs/map.json')2324 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 0)2526 ipfs.map('ipfsMapfileHash', 'processGravatar', Value.fromString('Gravatar'), ['json'])2728 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 3)29 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '1', 'displayName', 'Gravatar1')30 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '2', 'displayName', 'Gravatar2')31 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '3', 'displayName', 'Gravatar3')32})utils.ts file:
1import { Address, ethereum, JSONValue, Value, ipfs, json, Bytes } from "@graphprotocol/graph-ts"2import { Gravatar } from "../../generated/schema"34...56// ipfs.map callback7export function processGravatar(value: JSONValue, userData: Value): void {8 // See the JSONValue documentation for details on dealing9 // with JSON values10 let obj = value.toObject()11 let id = obj.get('id')1213 if (!id) {14 return15 }1617 // Callbacks can also created entities18 let gravatar = new Gravatar(id.toString())19 gravatar.displayName = userData.toString() + id.toString()20 gravatar.save()21}2223// function that calls ipfs.cat24export function gravatarFromIpfs(): void {25 let rawData = ipfs.cat("ipfsCatfileHash")2627 if (!rawData) {28 return29 }3031 let jsonData = json.fromBytes(rawData as Bytes).toObject()3233 let id = jsonData.get('id')34 let url = jsonData.get("imageUrl")3536 if (!id || !url) {37 return38 }3940 let gravatar = new Gravatar(id.toString())41 gravatar.imageUrl = url.toString()42 gravatar.save()43}断定存储的状态
用户能够通过断定实体断定存储的最终(或中途)状态。为此,用户必须提供实体类型、实体的特定ID、该实体上的字段名称以及字段的预期值。下面是一个快速示例:
1import { assert } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { Gravatar } from '../generated/schema'34let gravatar = new Gravatar('gravatarId0')5gravatar.save()67assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', 'gravatarId0', 'id', 'gravatarId0')正在运行assert.fieldEquals() 函数将检查给定字段的均等性与给定的预期值。 测试将失败,如果值为 NOT 则输出错误消息。否则测试将成功通过。
与事件元数据交互
用户可以使用 newMockEvent() 函数返回默认的交易元数据。事件可以使用 newMockEvent() 函数。 下面的示例显示您如何在事件对象上读/写到那些字段:
1// Read2let logType = newGravatarEvent.logType34// Write5let UPDATED_ADDRESS = '0xB16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A'6newGravatarEvent.address = Address.fromString(UPDATED_ADDRESS)断定变量相等
1assert.equals(ethereum.Value.fromString("hello"); ethereum.Value.fromString("hello"));断定实体不在存储中
用户可以断定实体在存储中不存在。该函数接受实体类型和id。如果实体实际上在存储中,测试将失败,并显示相关错误消息。以下是如何使用此功能的快速示例:
1assert.notInStore('Gravatar', '23')打印整个内存或单个实体(用于调试目的)
您可以使用此助手功能将整个存储登载到控制台:
1import { logStore } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'23logStore()从 0.6.0版本 logStore 不再打印派生字段,而是用户可以使用新的 logEntity 函数。 当然,logEntity可以用于打印任何实体,而不仅仅是有衍生字段的实体。 logEntity 需要实体类型、实体ID和一个showRelated标志来表示用户是否想打印相关派生实体。
1import { logEntity } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'234logEntity("Gravatar", 23, true)预期故障
使用test()函数上的shouldFail标志,用户可能会出现预期的测试失败:
1test(2 'Should throw an error',3 () => {4 throw new Error()5 },6 true,7)如果测试标记为should fail=true但不失败,则将在日志中显示为错误,测试区块将失败。此外,如果标记为shouldFail=false(默认状态),测试执行器将崩溃。
日志
在单元测试中记录自定义日志与在映射中记录完全相同。不同之处在于,日志对象需要从matchstick-as 而不是graph-ts导入。下面是一个所有非关键日志类型的简单示例:
1import { test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index";2import { log } from "matchstick-as/assembly/log";34test("Success", () => {5 log.success("Success!". []);6});7test("Error", () => {8 log.error("Error :( ", []);9});10test("Debug", () => {11 log.debug("Debugging...", []);12});13test("Info", () => {14 log.info("Info!", []);15});16test("Warning", () => {17 log.warning("Warning!", []);18});用户还可以模拟严重故障,如下所示:
1test('Blow everything up', () => {2 log.critical('Boom!')3})记录关键错误将停止测试的执行,并使一切崩溃。毕竟,我们希望确保您的代码在部署中没有关键日志,如果发生这种情况,您应该立即注意。
测试派生字段
测试派生字段是一个功能,用户可以在某个实体上设置一个字段,如果它从第一个实体中获得一个字段,则另一个实体会自动更新。
在版本 0.6.0 之前,可以通过以实体字段/属性访问它们来获取派生实体,就像这样:
1let entity = ExampleEntity.load('id')2let derivedEntity = entity.derived_entity截至版本0.6'。 , 通过使用graph节点的 loadRelated 函数来做到这一点, 派生的实体可以以与处理器相同的方式访问。
1test('Derived fields example test', () => {2 let mainAccount = GraphAccount.load('12')!34 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('nameSignalTransactions'))5 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('operatorOf'))67 let operatedAccount = GraphAccount.load('1')!8 operatedAccount.operators = [mainAccount.id]9 operatedAccount.save()1011 mockNameSignalTransaction('1234', mainAccount.id)12 mockNameSignalTransaction('2', mainAccount.id)1314 mainAccount = GraphAccount.load('12')!1516 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('nameSignalTransactions'))17 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('operatorOf'))1819 const nameSignalTransactions = mainAccount.nameSignalTransactions.load()20 const operatorsOfMainAccount = mainAccount.operatorOf.load()2122 assert.i32Equals(2, nameSignalTransactions.length)23 assert.i32Equals(1, operatorsOfMainAccount.length)2425 assert.stringEquals('1', operatorsOfMainAccount[0].id)2627 mockNameSignalTransaction('2345', mainAccount.id)2829 let nst = NameSignalTransaction.load('1234')!30 nst.signer = '11'31 nst.save()3233 store.remove('NameSignalTransaction', '2')3435 mainAccount = GraphAccount.load('12')!36 assert.i32Equals(1, mainAccount.nameSignalTransactions.load().length)37})测试 loadInBlock
从版本 0.6.0 开始,用户可以使用 mockInBlockStore 测试loadInBlock ,它允许在区块缓存中模拟实体。
1import { afterAll, beforeAll, describe, mockInBlockStore, test } from 'matchstick-as'2import { Gravatar } from '../../generated/schema'34describe('loadInBlock', () => {5 beforeAll(() => {6 mockInBlockStore('Gravatar', 'gravatarId0', gravatar)7 })89 afterAll(() => {10 clearInBlockStore()11 })1213 test('Can use entity.loadInBlock() to retrieve entity from cache store in the current block', () => {14 let retrievedGravatar = Gravatar.loadInBlock('gravatarId0')15 assert.stringEquals('gravatarId0', retrievedGravatar!.get('id')!.toString())16 })1718 test("Returns null when calling entity.loadInBlock() if an entity doesn't exist in the current block", () => {19 let retrievedGravatar = Gravatar.loadInBlock('IDoNotExist')20 assert.assertNull(retrievedGravatar)21 })22})测试动态数据源
可以通过模拟数据源命名空间的context()、address()和network()的返回值来测试动态数据源。 这些函数目前返回以下内容:context() - 返回一个空实体(DataSourceContext)、address() - 返回 0x000000000000000000000000、net() - 返回 mainnet 。 create(...) 和 createWidext(...) 两个函数都被嘲讽,完全不需要在测试中调用。 对返回值的更改可以通过matchstick-as中的dataSourceMock命名空间的函数进行(版本 0.3.0+)。
示例如下:
首先,我们有以下事件处理程序(它被有意地重新用于展示模拟数据源):
1export function handleApproveTokenDestinations(event: ApproveTokenDestinations): void {2 let tokenLockWallet = TokenLockWallet.load(dataSource.address().toHexString())!3 if (dataSource.network() == 'rinkeby') {4 tokenLockWallet.tokenDestinationsApproved = true5 }6 let context = dataSource.context()7 if (context.get('contextVal')!.toI32() > 0) {8 tokenLockWallet.setBigInt('tokensReleased', BigInt.fromI32(context.get('contextVal')!.toI32()))9 }10 tokenLockWallet.save()11}然后,我们使用dataSourceMock命名空间中的一个方法进行测试,为所有dataSource函数设置一个新返回值:
1import { assert, test, newMockEvent, dataSourceMock } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { BigInt, DataSourceContext, Value } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'34import { handleApproveTokenDestinations } from '../../src/token-lock-wallet'5import { ApproveTokenDestinations } from '../../generated/templates/GraphTokenLockWallet/GraphTokenLockWallet'6import { TokenLockWallet } from '../../generated/schema'78test('Data source simple mocking example', () => {9 let addressString = '0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A'10 let address = Address.fromString(addressString)1112 let wallet = new TokenLockWallet(address.toHexString())13 wallet.save()14 let context = new DataSourceContext()15 context.set('contextVal', Value.fromI32(325))16 dataSourceMock.setReturnValues(addressString, 'rinkeby', context)17 let event = changetype<ApproveTokenDestinations>(newMockEvent())1819 assert.assertTrue(!wallet.tokenDestinationsApproved)2021 handleApproveTokenDestinations(event)2223 wallet = TokenLockWallet.load(address.toHexString())!24 assert.assertTrue(wallet.tokenDestinationsApproved)25 assert.bigIntEquals(wallet.tokensReleased, BigInt.fromI32(325))2627 dataSourceMock.resetValues()28})注意,dataSourceMock.resetValues()在末尾被调用。这是因为值在更改时会被记住,如果要返回到默认值,则需要重新设置。
测试动态数据源创建
从版本 0.6.0 开始,可以测试是否从模板创建了一个新的数据源。 此功能支持etherum/contract 和 file/ipfs 模板。为此有四个函数:
assert.dataSourceCount(templateName,expectedCount)可以用来确定指定模板中的数据源的预期数量assert. ataSourceExists(templateName) address/ipfsHash)声称,从一个指定的模板创建了带有指定标识符的数据源(可以是合约地址或IPFS 文件哈希)logDataSources(templateName)将指定模板中的所有数据源打印到控制台以进行调试readFile(path)读取一个 JSON 文件,表示一个 IPFS 文件,并返回内容为字节
测试etherum/contract模板
1test('ethereum/contract dataSource creation example', () => {2 // Assert there are no dataSources created from GraphTokenLockWallet template3 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 0)45 // Create a new GraphTokenLockWallet datasource with address 0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A6 GraphTokenLockWallet.create(Address.fromString('0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A'))78 // Assert the dataSource has been created9 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 1)1011 // Add a second dataSource with context12 let context = new DataSourceContext()13 context.set('contextVal', Value.fromI32(325))1415 GraphTokenLockWallet.createWithContext(Address.fromString('0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2B'), context)1617 // Assert there are now 2 dataSources18 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 2)1920 // Assert that a dataSource with address "0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2B" was created21 // Keep in mind that `Address` type is transformed to lower case when decoded, so you have to pass the address as all lower case when asserting if it exists22 assert.dataSourceExists('GraphTokenLockWallet', '0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2B'.toLowerCase())2324 logDataSources('GraphTokenLockWallet')25})示例 logDataSource 输出
1🛠 {2 "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2a": {3 "kind": "ethereum/contract",4 "name": "GraphTokenLockWallet",5 "address": "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2a",6 "context": null7 },8 "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2b": {9 "kind": "ethereum/contract",10 "name": "GraphTokenLockWallet",11 "address": "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2b",12 "context": {13 "contextVal": {14 "type": "Int",15 "data": 32516 }17 }18 }19}测试file/ipfs模板
类似于合约动态数据源,用户可以测试文件数据源及其处理程序
示例 subgraph.yaml
1...2templates:3 - kind: file/ipfs4 name: GraphTokenLockMetadata5 network: mainnet6 mapping:7 kind: ethereum/events8 apiVersion: 0.0.99 language: wasm/assemblyscript10 file: ./src/token-lock-wallet.ts11 handler: handleMetadata12 entities:13 - TokenLockMetadata14 abis:15 - name: GraphTokenLockWallet16 file: ./abis/GraphTokenLockWallet.json示例 schema.graphql
1"""2Token Lock Wallets which hold locked GRT3"""4type TokenLockMetadata @entity {5 "The address of the token lock wallet"6 id: ID!7 "Start time of the release schedule"8 startTime: BigInt!9 "End time of the release schedule"10 endTime: BigInt!11 "Number of periods between start time and end time"12 periods: BigInt!13 "Time when the releases start"14 releaseStartTime: BigInt!15}示例 metadata.json
1{2 "startTime": 1,3 "endTime": 1,4 "periods": 1,5 "releaseStartTime": 16}示例处理程序:
1export function handleMetadata(content: Bytes): void {2 // dataSource.stringParams() returns the File DataSource CID3 // stringParam() will be mocked in the handler test4 // for more info https://thegraph.com/docs/en/developing/creating-a-subgraph/#create-a-new-handler-to-process-files5 let tokenMetadata = new TokenLockMetadata(dataSource.stringParam())6 const value = json.fromBytes(content).toObject()78 if (value) {9 const startTime = value.get('startTime')10 const endTime = value.get('endTime')11 const periods = value.get('periods')12 const releaseStartTime = value.get('releaseStartTime')1314 if (startTime && endTime && periods && releaseStartTime) {15 tokenMetadata.startTime = startTime.toBigInt()16 tokenMetadata.endTime = endTime.toBigInt()17 tokenMetadata.periods = periods.toBigInt()18 tokenMetadata.releaseStartTime = releaseStartTime.toBigInt()19 }2021 tokenMetadata.save()22 }23}Example test
1import { assert, test, dataSourceMock, readFile } from 'matchstick-as'2import { Address, BigInt, Bytes, DataSourceContext, ipfs, json, store, Value } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'34import { handleMetadata } from '../../src/token-lock-wallet'5import { TokenLockMetadata } from '../../generated/schema'6import { GraphTokenLockMetadata } from '../../generated/templates'78test('file/ipfs dataSource creation example', () => {9 // Generate the dataSource CID from the ipfsHash + ipfs path file10 // For example QmaXzZhcYnsisuue5WRdQDH6FDvqkLQX1NckLqBYeYYEfm/example.json11 const ipfshash = 'QmaXzZhcYnsisuue5WRdQDH6FDvqkLQX1NckLqBYeYYEfm'12 const CID = `${ipfshash}/example.json`1314 // Create a new dataSource using the generated CID15 GraphTokenLockMetadata.create(CID)1617 // Assert the dataSource has been created18 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockMetadata', 1)19 assert.dataSourceExists('GraphTokenLockMetadata', CID)20 logDataSources('GraphTokenLockMetadata')2122 // Now we have to mock the dataSource metadata and specifically dataSource.stringParam()23 // dataSource.stringParams actually uses the value of dataSource.address(), so we will mock the address using dataSourceMock from matchstick-as24 // First we will reset the values and then use dataSourceMock.setAddress() to set the CID25 dataSourceMock.resetValues()26 dataSourceMock.setAddress(CID)2728 // Now we need to generate the Bytes to pass to the dataSource handler29 // For this case we introduced a new function readFile, that reads a local json and returns the content as Bytes30 const content = readFile(`path/to/metadata.json`)31 handleMetadata(content)3233 // Now we will test if a TokenLockMetadata was created34 const metadata = TokenLockMetadata.load(CID)3536 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.endTime, BigInt.fromI32(1))37 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.periods, BigInt.fromI32(1))38 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.releaseStartTime, BigInt.fromI32(1))39 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.startTime, BigInt.fromI32(1))40})测试覆盖率
使用Matchstick,子图开发者可以运行一个脚本,计算编写的单元测试的测试覆盖率。
测试覆盖工具接受已编译的测试 wasm 二进制并将它们转换为 wat 文件, 然后便于检查,看看是否subgraph.yaml中定义的处理程序已被调用。 因为代码覆盖面(和整个测试)在 AssemblyScript 和 WebAssembly 中处于早期阶段,Matchstick 无法检查分支覆盖面。 相反,我们依赖的是这样一种说法:如果一个处理程序被调用了,它的事件/功能就被恰当地仿效了。
先决条件
要运行在 Matchstick* 中提供的测试覆盖功能,您需要事先准备几件事:
导出处理程序
为了让Matchstick 检查哪些处理程序正在运行,这些处理程序需要从 测试文件 导出。 因此,例如在我们的例子中,在我们的gravity.test.ts文件中,我们有以下处理程序被导入:
1import { handleNewGravatar } from '../../src/gravity'为了让这个函数可见,我们也需要导出它(以名字写入wat文件)。 像这样:
1export { handleNewGravatar }使用方法
设置好后,要运行测试覆盖工具,只需运行:
1graph test -- -c你也可以在你的 package.json 文件中添加一个自定义的 coverage 命令,就像这样:
1"scripts": {2 /.../3 "coverage": "graph test -- -c"4 },希望这可以毫无问题地执行覆盖工具。您应该在终端中看到类似的内容:
1$ graph test -c2Skipping download/install step because binary already exists at /Users/petko/work/demo-subgraph/node_modules/binary-install-raw/bin/0.4.034___ ___ _ _ _ _ _5| \/ | | | | | | | (_) | |6| . . | __ _| |_ ___| |__ ___| |_ _ ___| | __7| |\/| |/ _` | __/ __| '_ \/ __| __| |/ __| |/ /8| | | | (_| | || (__| | | \__ \ |_| | (__| <9\_| |_/\__,_|\__\___|_| |_|___/\__|_|\___|_|\_\1011Compiling...1213Running in coverage report mode.14 ️15Reading generated test modules... 🔎️1617Generating coverage report 📝1819Handlers for source 'Gravity':20Handler 'handleNewGravatar' is tested.21Handler 'handleUpdatedGravatar' is not tested.22Handler 'handleCreateGravatar' is tested.23Test coverage: 66.7% (2/3 handlers).2425Handlers for source 'GraphTokenLockWallet':26Handler 'handleTokensReleased' is not tested.27Handler 'handleTokensWithdrawn' is not tested.28Handler 'handleTokensRevoked' is not tested.29Handler 'handleManagerUpdated' is not tested.30Handler 'handleApproveTokenDestinations' is not tested.31Handler 'handleRevokeTokenDestinations' is not tested.32Test coverage: 0.0% (0/6 handlers).3334Global test coverage: 22.2% (2/9 handlers).日志输出中的测试运行持续时间
日志输出包括测试运行持续时间。下面是一个示例:
常见编译器错误
关键:无法从具有背景的有效模块创建WasmInstance:未知导入:wasi_snapshot_preview1::尚未定义fd_write
这意味着您在代码中使用了console.log,不被 AssemblyScript 支持。请考虑使用 日志API。
ERROR TS2554: Expected ? arguments, but got ?.
返回ethereum.Block(defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddress, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt);
in ~lib/matchstick-as/assembly/defaults.ts(18,12)
ERROR TS2554: Expected ? arguments, but got ?.
返回新ethereum.Transaction(defaultAddressBytes, defaultBigInt, defaultAddress, defaultAddress, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultAddressBytes, defaultBigInt);
in ~lib/matchstick-as/assembly/defaults.ts(24,12)
参数中的不匹配是由graph-ts和matchstick-as中的不匹配造成的。 解决这类问题的最佳方法是更新最新发布的版本。
其他资源
如需任何额外支持,请查看此使用Matchstick的演示子图仓库。
反馈
如果您有任何问题、反馈、特征请求或只是想与我们联系,最好的地方是 Graph Discord,我们有一个专门的 Matchstick 频道,名为 🔥| 单元测试。