25 dakika
Birim Testi Framework'ü
Learn how to use Matchstick, a unit testing framework developed by LimeChain. Matchstick enables Subgraph developers to test their mapping logic in a sandboxed environment and successfully deploy their Subgraphs.
Benefits of Using Matchstick
- It’s written in Rust and optimized for high performance.
- It gives you access to developer features, including the ability to mock contract calls, make assertions about the store state, monitor Subgraph failures, check test performance, and many more.
Buradan Başlayın
Install Dependencies
In order to use the test helper methods and run tests, you need to install the following dependencies:
1yarn add --dev matchstick-asInstall PostgreSQL
graph-node depends on PostgreSQL, so if you don’t already have it, then you will need to install it.
Note: It’s highly recommended to use the commands below to avoid unexpected errors.
Using MacOS
Installation command:
1brew install postgresqlCreate a symlink to the latest libpq.5.lib You may need to create this dir first /usr/local/opt/postgresql/lib/
1ln -sf /usr/local/opt/postgresql@14/lib/postgresql@14/libpq.5.dylib /usr/local/opt/postgresql/lib/libpq.5.dylibUsing Linux
Installation command (depends on your distro):
1sudo apt install postgresqlUsing WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux)
Matchstick’i WSL’de Docker yaklaşımı ve ikili yaklaşımı kullanarak kullanabilirsiniz. WSL biraz alengirli olabileceğinden, aşağıdaki gibi sorunlarla karşılaşırsanız birkaç ipucu verelim
1static BYTES = Symbol("Bytes") SyntaxError: Unexpected token =yada
1<PROJECT_PATH>/node_modules/gluegun/build/index.js:13 throw up;Please make sure you’re on a newer version of Node.js graph-cli doesn’t support v10.19.0 anymore, and that is still the default version for new Ubuntu images on WSL. For instance Matchstick is confirmed to be working on WSL with v18.1.0, you can switch to it either via nvm or if you update your global Node.js. Don’t forget to delete node_modules and to run npm install again after updating you nodejs! Then, make sure you have libpq installed, you can do that by running
1sudo apt-get install libpq-devAnd finally, do not use graph test (which uses your global installation of graph-cli and for some reason that looks like it’s broken on WSL currently), instead use yarn test or npm run test (that will use the local, project-level instance of graph-cli, which works like a charm). For that you would of course need to have a "test" script in your package.json file which can be something as simple as
1{2 "name": "demo-subgraph",3 "version": "0.1.0",4 "scripts": {5 "test": "graph test",6 ...7 },8 "dependencies": {9 "@graphprotocol/graph-cli": "^0.56.0",10 "@graphprotocol/graph-ts": "^0.31.0",11 "matchstick-as": "^0.6.0"12 }13}Using Matchstick
To use Matchstick in your Subgraph project just open up a terminal, navigate to the root folder of your project and simply run graph test [options] <datasource> - it downloads the latest Matchstick binary and runs the specified test or all tests in a test folder (or all existing tests if no datasource flag is specified).
CLI seçenekleri
Bu, test klasöründeki tüm testleri çalıştıracaktır:
1graph testBu, gravity.test.ts adında bir testi ve/veya gravity adında bir klasördeki tüm testleri çalıştıracaktır:
1graph test gravityBu sadece belirtilen test dosyasını çalıştıracaktır:
1graph test path/to/file.test.tsOptions:
1-c, --coverage Run the tests in coverage mode2-d, --docker Run the tests in a docker container (Note: Please execute from the root folder of the Subgraph)3-f, --force Binary: Redownloads the binary. Docker: Redownloads the Dockerfile and rebuilds the docker image.4-h, --help Show usage information5-l, --logs Logs to the console information about the OS, CPU model and download url (debugging purposes)6-r, --recompile Forces tests to be recompiled7-v, --version <tag> Choose the version of the rust binary that you want to be downloaded/usedDocker
From graph-cli 0.25.2, the graph test command supports running matchstick in a docker container with the -d flag. The docker implementation uses bind mount so it does not have to rebuild the docker image every time the graph test -d command is executed. Alternatively you can follow the instructions from the matchstick repository to run docker manually.
❗ graph test -d forces docker run to run with flag -t. This must be removed to run inside non-interactive environments (like GitHub CI).
❗ If you have previously ran graph test you may encounter the following error during docker build:
1error from sender: failed to xattr node_modules/binary-install-raw/bin/binary-<platform>: permission deniedIn this case create a .dockerignore in the root folder and add node_modules/binary-install-raw/bin
Yapılandırma
Matchstick can be configured to use a custom tests, libs and manifest path via matchstick.yaml config file:
1testsFolder: path/to/tests2libsFolder: path/to/libs3manifestPath: path/to/subgraph.yamlDemo Subgraph
You can try out and play around with the examples from this guide by cloning the Demo Subgraph repo
Öğretici videolar
Also you can check out the video series on “How to use Matchstick to write unit tests for your Subgraphs”
Test yapısı
IMPORTANT: The test structure described below depends on matchstick-as version >=0.5.0
describe()
describe(name: String , () => {}) - Defines a test group.
Notes:
- Açıklamalar zorunlu değildir. Hala test() fonksiyonunu describe() bloklarının dışında kullanabilirsiniz
Örnek:
1import { describe, test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar()", () => {5 test("Should create a new Gravatar entity", () => {6 ...7 })8})Nested describe() example:
1import { describe, test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleUpdatedGravatar()", () => {5 describe("When entity exists", () => {6 test("updates the entity", () => {7 ...8 })9 })1011 describe("When entity does not exists", () => {12 test("it creates a new entity", () => {13 ...14 })15 })16})test()
test(name: String, () =>, should_fail: bool) - Defines a test case. You can use test() inside of describe() blocks or independently.
Örnek:
1import { describe, test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar()", () => {5 test("Should create a new Entity", () => {6 ...7 })8})yada
1test("handleNewGravatar() should create a new entity", () => {2 ...3})beforeAll()
Runs a code block before any of the tests in the file. If beforeAll is declared inside of a describe block, it runs at the beginning of that describe block.
Örnekler:
Code inside beforeAll will execute once before all tests in the file.
1import { describe, test, beforeAll } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"3import { Gravatar } from "../../generated/schema"45beforeAll(() => {6 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")7 gravatar.displayName = “First Gravatar”8 gravatar.save()9 ...10})1112describe("When the entity does not exist", () => {13 test("it should create a new Gravatar with id 0x1", () => {14 ...15 })16})1718describe("When entity already exists", () => {19 test("it should update the Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {20 ...21 })22})Code inside beforeAll will execute once before all tests in the first describe block
1import { describe, test, beforeAll } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"3import { Gravatar } from "../../generated/schema"45describe("handleUpdatedGravatar()", () => {6 beforeAll(() => {7 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")8 gravatar.displayName = “First Gravatar”9 gravatar.save()10 ...11 })1213 test("updates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {14 ...15 })1617 test("creates new Gravatar with id 0x1", () => {18 ...19 })20})afterAll()
Runs a code block after all of the tests in the file. If afterAll is declared inside of a describe block, it runs at the end of that describe block.
Örnek:
Code inside afterAll will execute once after all tests in the file.
1import { describe, test, afterAll } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"3import { store } from "@graphprotocol/graph-ts"45afterAll(() => {6 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x0")7 ...8})910describe("handleNewGravatar, () => {11 test("creates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {12 ...13 })14})1516describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {17 test("updates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {18 ...19 })20})Code inside afterAll will execute once after all tests in the first describe block
1import { describe, test, afterAll, clearStore } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar", () => {5 afterAll(() => {6 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x1")7 ...8 })910 test("It creates a new entity with Id 0x0", () => {11 ...12 })1314 test("It creates a new entity with Id 0x1", () => {15 ...16 })17})1819describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {20 test("updates Gravatar with id 0x0", () => {21 ...22 })23})beforeEach()
Runs a code block before every test. If beforeEach is declared inside of a describe block, it runs before each test in that describe block.
Examples: Code inside beforeEach will execute before each tests.
1import { describe, test, beforeEach, clearStore } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleNewGravatars } from "./utils"34beforeEach(() => {5 clearStore() // <-- clear the store before each test in the file6})78describe("handleNewGravatars, () => {9 test("A test that requires a clean store", () => {10 ...11 })1213 test("Second that requires a clean store", () => {14 ...15 })16})1718 ...Code inside beforeEach will execute only before each test in the that describe
1import { describe, test, beforeEach } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from '../../src/gravity'34describe('handleUpdatedGravatars', () => {5 beforeEach(() => {6 let gravatar = new Gravatar('0x0')7 gravatar.displayName = 'First Gravatar'8 gravatar.imageUrl = ''9 gravatar.save()10 })1112 test('Updates the displayName', () => {13 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'displayName', 'First Gravatar')1415 // code that should update the displayName to 1st Gravatar1617 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'displayName', '1st Gravatar')18 store.remove('Gravatar', '0x0')19 })2021 test('Updates the imageUrl', () => {22 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'imageUrl', '')2324 // code that should changes the imageUrl to https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x02526 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x0', 'imageUrl', 'https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x0')27 store.remove('Gravatar', '0x0')28 })29})afterEach()
Runs a code block after every test. If afterEach is declared inside of a describe block, it runs after each test in that describe block.
Örnekler:
Code inside afterEach will execute after every test.
1import { describe, test, beforeEach, afterEach } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34beforeEach(() => {5 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")6 gravatar.displayName = “First Gravatar”7 gravatar.save()8})910afterEach(() => {11 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x0")12})1314describe("handleNewGravatar", () => {15 ...16})1718describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {19 test("Updates the displayName", () => {20 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "First Gravatar")2122 // code that should update the displayName to 1st Gravatar2324 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "1st Gravatar")25 })2627 test("Updates the imageUrl", () => {28 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "")2930 // code that should changes the imageUrl to https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x03132 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x0")33 })34})Code inside afterEach will execute after each test in that describe
1import { describe, test, beforeEach, afterEach } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index"2import { handleUpdatedGravatar, handleNewGravatar } from "../../src/gravity"34describe("handleNewGravatar", () => {5 ...6})78describe("handleUpdatedGravatar", () => {9 beforeEach(() => {10 let gravatar = new Gravatar("0x0")11 gravatar.displayName = "First Gravatar"12 gravatar.imageUrl = ""13 gravatar.save()14 })1516 afterEach(() => {17 store.remove("Gravatar", "0x0")18 })1920 test("Updates the displayName", () => {21 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "First Gravatar")2223 // code that should update the displayName to 1st Gravatar2425 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "displayName", "1st Gravatar")26 })2728 test("Updates the imageUrl", () => {29 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "")3031 // code that should changes the imageUrl to https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x03233 assert.fieldEquals("Gravatar", "0x0", "imageUrl", "https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/0x0")34 })35})Açıklamalar
1fieldEquals(entityType: string, id: string, fieldName: string, expectedVal: string)23equals(expected: ethereum.Value, actual: ethereum.Value)45notInStore(entityType: string, id: string)67addressEquals(address1: Address, address2: Address)89bytesEquals(bytes1: Bytes, bytes2: Bytes)1011i32Equals(number1: i32, number2: i32)1213bigIntEquals(bigInt1: BigInt, bigInt2: BigInt)1415booleanEquals(bool1: boolean, bool2: boolean)1617stringEquals(string1: string, string2: string)1819arrayEquals(array1: Array<ethereum.Value>, array2: Array<ethereum.Value>)2021tupleEquals(tuple1: ethereum.Tuple, tuple2: ethereum.Tuple)2223assertTrue(value: boolean)2425assertNull<T>(value: T)2627assertNotNull<T>(value: T)2829entityCount(entityType: string, expectedCount: i32)Sürüm 0.6.0 itibariyle, assert fonksiyonları özel hata mesajlarını da desteklemektedir
1assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '0x123', 'id', '0x123', 'Id should be 0x123')2assert.equals(ethereum.Value.fromI32(1), ethereum.Value.fromI32(1), 'Value should equal 1')3assert.notInStore('Gravatar', '0x124', 'Gravatar should not be in store')4assert.addressEquals(Address.zero(), Address.zero(), 'Address should be zero')5assert.bytesEquals(Bytes.fromUTF8('0x123'), Bytes.fromUTF8('0x123'), 'Bytes should be equal')6assert.i32Equals(2, 2, 'I32 should equal 2')7assert.bigIntEquals(BigInt.fromI32(1), BigInt.fromI32(1), 'BigInt should equal 1')8assert.booleanEquals(true, true, 'Boolean should be true')9assert.stringEquals('1', '1', 'String should equal 1')10assert.arrayEquals([ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)], [ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)], 'Arrays should be equal')11assert.tupleEquals(12 changetype<ethereum.Tuple>([ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)]),13 changetype<ethereum.Tuple>([ethereum.Value.fromI32(1)]),14 'Tuples should be equal',15)16assert.assertTrue(true, 'Should be true')17assert.assertNull(null, 'Should be null')18assert.assertNotNull('not null', 'Should be not null')19assert.entityCount('Gravatar', 1, 'There should be 2 gravatars')20assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 1, 'GraphTokenLockWallet template should have one data source')21assert.dataSourceExists(22 'GraphTokenLockWallet',23 Address.zero().toHexString(),24 'GraphTokenLockWallet should have a data source for zero address',25)Bir Birim Testi Yazın
Let’s see how a simple unit test would look like using the Gravatar examples in the Demo Subgraph.
Aşağıdaki işleyici fonksiyonuna sahip olduğumuzu varsayarsak (iki yardımcı işlevle birlikte):
1export function handleNewGravatar(event: NewGravatar): void {2 let gravatar = new Gravatar(event.params.id.toHex())3 gravatar.owner = event.params.owner4 gravatar.displayName = event.params.displayName5 gravatar.imageUrl = event.params.imageUrl6 gravatar.save()7}89export function handleNewGravatars(events: NewGravatar[]): void {10 events.forEach((event) => {11 handleNewGravatar(event)12 })13}1415export function createNewGravatarEvent(16 id: i32,17 ownerAddress: string,18 displayName: string,19 imageUrl: string,20): NewGravatar {21 let mockEvent = newMockEvent()22 let newGravatarEvent = new NewGravatar(23 mockEvent.address,24 mockEvent.logIndex,25 mockEvent.transactionLogIndex,26 mockEvent.logType,27 mockEvent.block,28 mockEvent.transaction,29 mockEvent.parameters,30 )31 newGravatarEvent.parameters = new Array()32 let idParam = new ethereum.EventParam('id', ethereum.Value.fromI32(id))33 let addressParam = new ethereum.EventParam(34 'ownerAddress',35 ethereum.Value.fromAddress(Address.fromString(ownerAddress)),36 )37 let displayNameParam = new ethereum.EventParam('displayName', ethereum.Value.fromString(displayName))38 let imageUrlParam = new ethereum.EventParam('imageUrl', ethereum.Value.fromString(imageUrl))3940 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(idParam)41 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(addressParam)42 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(displayNameParam)43 newGravatarEvent.parameters.push(imageUrlParam)4445 return newGravatarEvent46}Önce projemizde bir test dosyası oluşturmamız gerekiyor. Bunun nasıl görünebileceğine dair bir örnek:
1import { clearStore, test, assert } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { Gravatar } from '../../generated/schema'3import { NewGravatar } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'4import { createNewGravatarEvent, handleNewGravatars } from '../mappings/gravity'56test('Can call mappings with custom events', () => {7 // Create a test entity and save it in the store as initial state (optional)8 let gravatar = new Gravatar('gravatarId0')9 gravatar.save()1011 // Create mock events12 let newGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(12345, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')13 let anotherGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(3546, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')1415 // Call mapping functions passing the events we just created16 handleNewGravatars([newGravatarEvent, anotherGravatarEvent])1718 // Assert the state of the store19 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', 'gravatarId0', 'id', 'gravatarId0')20 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '12345', 'owner', '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7')21 assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', '3546', 'displayName', 'cap')2223 // Clear the store in order to start the next test off on a clean slate24 clearStore()25})2627test('Next test', () => {28 //...29})That’s a lot to unpack! First off, an important thing to notice is that we’re importing things from matchstick-as, our AssemblyScript helper library (distributed as an npm module). You can find the repository here. matchstick-as provides us with useful testing methods and also defines the test() function which we will use to build our test blocks. The rest of it is pretty straightforward - here’s what happens:
- İlk durumumuzu ayarlıyor ve bir özel Gravatar varlığı ekliyoruz;
- We define two
NewGravatarevent objects along with their data, using thecreateNewGravatarEvent()function; - We’re calling out handler methods for those events -
handleNewGravatars()and passing in the list of our custom events; - Depo durumunu doğruluyoruz. Bu nasıl çalışır? - Bir varlık türü ve kimliğinin benzersiz bir kombinasyonunu geçiriyoruz. Ardından, bu varlıkta belirli bir alanı kontrol ediyoruz ve beklediğimiz değeri almasını sağlıyoruz. Hem depoya eklediğimiz ilk Gravatar Varlığı için hem de işleyici işlevi çağrıldığında eklenen iki Gravatar varlığı için bunu yapıyoruz;
- And lastly - we’re cleaning the store using
clearStore()so that our next test can start with a fresh and empty store object. We can define as many test blocks as we want.
İşte başardın - ilk testimizi oluşturduk! 👏
Now in order to run our tests you simply need to run the following in your Subgraph root folder:
graph test Gravity
Ve her şey yolunda giderse aşağıdakiyle karşılaşacaksınız:
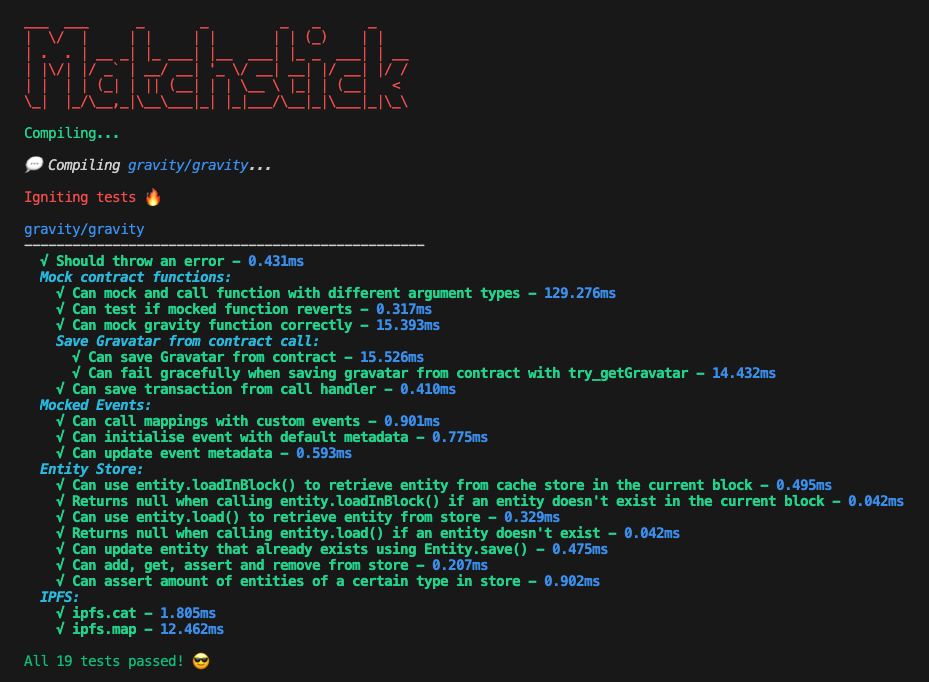
Çok rastlanan test senaryoları
Belirli bir durumla depoyu doldurma
Kullanıcılar bilinen bir varlık kümesiyle depoyu doldurabilirler. Aşağıdaki örnek depoyu Gravatar varlığıyla başlatmak için kullanılabilir:
1let gravatar = new Gravatar('entryId')2gravatar.save()Olayla bir eşleştirme fonksiyonu çağırmak
Kullanıcı, depoya bağlı bir eşleştirme fonksiyonuna özel bir olay oluşturabilir ve onu iletebilir:
1import { store } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'2import { NewGravatar } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'3import { handleNewGravatars, createNewGravatarEvent } from './mapping'45let newGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(12345, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')67handleNewGravatar(newGravatarEvent)Tüm eşitlemeleri olay fikstürleriyle çağırmak
Kullanıcılar test fikstürleriyle eşleştirmeleri çağırabilirler.
1import { NewGravatar } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'2import { store } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'3import { handleNewGravatars, createNewGravatarEvent } from './mapping'45let newGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(12345, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')67let anotherGravatarEvent = createNewGravatarEvent(3546, '0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7', 'cap', 'pac')89handleNewGravatars([newGravatarEvent, anotherGravatarEvent])1export function handleNewGravatars(events: NewGravatar[]): void {2 events.forEach(event => {3 handleNewGravatar(event);4 });5}Kontrat çağrılarını mocklama
Kullanıcılar sözleşme çağrılarını mocklayabilir:
1import { addMetadata, assert, createMockedFunction, clearStore, test } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { Gravity } from '../../generated/Gravity/Gravity'3import { Address, BigInt, ethereum } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'45let contractAddress = Address.fromString('0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7')6let expectedResult = Address.fromString('0x90cBa2Bbb19ecc291A12066Fd8329D65FA1f1947')7let bigIntParam = BigInt.fromString('1234')8createMockedFunction(contractAddress, 'gravatarToOwner', 'gravatarToOwner(uint256):(address)')9 .withArgs([ethereum.Value.fromSignedBigInt(bigIntParam)])10 .returns([ethereum.Value.fromAddress(Address.fromString('0x90cBa2Bbb19ecc291A12066Fd8329D65FA1f1947'))])1112let gravity = Gravity.bind(contractAddress)13let result = gravity.gravatarToOwner(bigIntParam)1415assert.equals(ethereum.Value.fromAddress(expectedResult), ethereum.Value.fromAddress(result))Gösterildiği gibi, bir sözleşme çağrısını mocklamak ve bir dönüş değeri sabitlemek için kullanıcı, bir sözleşme adresi, işlev adı, işlev imzası, bir argüman dizisi ve elbette dönüş değerini sağlamalıdır.
Kullanıcılar ayrıca fonksiyon geri çevirilerinide mocklayabilirler:
1let contractAddress = Address.fromString('0x89205A3A3b2A69De6Dbf7f01ED13B2108B2c43e7')2createMockedFunction(contractAddress, 'getGravatar', 'getGravatar(address):(string,string)')3 .withArgs([ethereum.Value.fromAddress(contractAddress)])4 .reverts()IPFS dosyalarını mocklama (Matchstick 0.4.1’den)
Users can mock IPFS files by using mockIpfsFile(hash, filePath) function. The function accepts two arguments, the first one is the IPFS file hash/path and the second one is the path to a local file.
NOTE: When testing ipfs.map/ipfs.mapJSON, the callback function must be exported from the test file in order for matchstick to detect it, like the processGravatar() function in the test example bellow:
.test.ts file:
1import { assert, test, mockIpfsFile } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { ipfs } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'3import { gravatarFromIpfs } from './utils'45// Export ipfs.map() callback in order for matchstick to detect it6export { processGravatar } from './utils'78test('ipfs.cat', () => {9 mockIpfsFile('ipfsCatfileHash', 'tests/ipfs/cat.json')1011 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 0)1213 gravatarFromIpfs()1415 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 1)16 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '1', 'imageUrl', 'https://i.ytimg.com/vi/MELP46s8Cic/maxresdefault.jpg')1718 clearStore()19})2021test('ipfs.map', () => {22 mockIpfsFile('ipfsMapfileHash', 'tests/ipfs/map.json')2324 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 0)2526 ipfs.map('ipfsMapfileHash', 'processGravatar', Value.fromString('Gravatar'), ['json'])2728 assert.entityCount(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, 3)29 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '1', 'displayName', 'Gravatar1')30 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '2', 'displayName', 'Gravatar2')31 assert.fieldEquals(GRAVATAR_ENTITY_TYPE, '3', 'displayName', 'Gravatar3')32})utils.ts file:
1import { Address, ethereum, JSONValue, Value, ipfs, json, Bytes } from "@graphprotocol/graph-ts"2import { Gravatar } from "../../generated/schema"34...56// ipfs.map geri çağrısı7export function processGravatar(value: JSONValue, userData: Value): void {8 // İşlem yapmayla ilgili ayrıntılar için JSONValue belgelerine bakın9 // JSON değerleri ile10 let obj = value.toObject()11 let id = obj.get('id')1213 if (!id) {14 return15 }1617 // Geri çağrılar ayrıca varlıklar oluşturabilir18 let gravatar = new Gravatar(id.toString())19 gravatar.displayName = userData.toString() + id.toString()20 gravatar.save()21}2223// ipfs.cat'i çağıran fonksiyon24export function gravatarFromIpfs(): void {25 let rawData = ipfs.cat("ipfsCatfileHash")2627 if (!rawData) {28 return29 }3031 let jsonData = json.fromBytes(rawData as Bytes).toObject()3233 let id = jsonData.get('id')34 let url = jsonData.get("imageUrl")3536 if (!id || !url) {37 return38 }3940 let gravatar = new Gravatar(id.toString())41 gravatar.imageUrl = url.toString()42 gravatar.save()43}Depo durumunu doğrulama
Kullanıcılar, varlıkları doğrulayarak deponun nihai (veya orta) durumunu doğrulayabilirler. Bunun için, kullanıcı bir Varlık türü, bir Varlığın belirli bir kimliği, o Varlıktaki bir alanın adı ve alanın beklenen değerini sağlamalıdır. Hızlıca bir örneğe bakalım:
1import { assert } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { Gravatar } from '../generated/schema'34let gravatar = new Gravatar('gravatarId0')5gravatar.save()67assert.fieldEquals('Gravatar', 'gravatarId0', 'id', 'gravatarId0')Running the assert.fieldEquals() function will check for equality of the given field against the given expected value. The test will fail and an error message will be outputted if the values are NOT equal. Otherwise the test will pass successfully.
Olay üst verileriyle etkileşim
Users can use default transaction metadata, which could be returned as an ethereum.Event by using the newMockEvent() function. The following example shows how you can read/write to those fields on the Event object:
1// Okuma2let logType = newGravatarEvent.logType34// Yazma5let UPDATED_ADDRESS = '0xB16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A'6newGravatarEvent.address = Address.fromString(UPDATED_ADDRESS)Değişken eşitliğini doğrulama
1assert.equals(ethereum.Value.fromString("hello"); ethereum.Value.fromString("hello"));Asserting that an Entity is not in the store
Kullanıcılar, bir varlığın depoda olmadığını doğrulayabilirler. Bu fonksiyon, bir varlık türü ve bir kimlik alır. Eğer varlık gerçekten depoda ise, test ilgili bir hata mesajı vererej başarısız olacaktır. Fonksiyonun nasıl kullanılacağına dair hızlıca bir örneğe bakalım:
1assert.notInStore('Gravatar', '23')Tüm mağazayı veya tüm mağazadan tek varlıkları yazdırma (hata ayıklama amaçlı)
Bu yardımcı fonksiyon kullanılarak deponun tamamı konsola yazdırılabilir:
1import { logStore } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'23logStore()As of version 0.6.0, logStore no longer prints derived fields, instead users can use the new logEntity function. Of course logEntity can be used to print any entity, not just ones that have derived fields. logEntity takes the entity type, entity id and a showRelated flag to indicate if users want to print the related derived entities.
1import { logEntity } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/store'234logEntity("Gravatar", 23, true)Beklenen başarısızlık
Kullanıcılar, shouldFail bayrağını test() fonksiyonlarında kullanarak beklenen test başarısızlıklarına sahip olabilirler:
1test(2 'Should throw an error',3 () => {4 throw new Error()5 },6 true,7)Test, shouldFail = true olarak işaretlenirse ama BAŞARISIZ olmazsa, bu kayıtlarda bir hata olarak görünecek ve test bloğu başarısız olacaktır. Ayrıca, with shouldFail = false (the default state) olarak işaretlenirse, test yürütücüsü çökecektir.
Kayıt tutma
Birim testlerinde özel kayıt tutmanın eşitlemelerdeki kayıt tutmaktan tamamen aynıdır. Fark, günlük nesnesinin graph-ts yerine matchstick-as’dan içe aktarılması gerektmesidir. İşte tüm kritik olmayan kayıt türleriyle ilgili basit bir örnek:
1import { test } from "matchstick-as/assembly/index";2import { log } from "matchstick-as/assembly/log";34test("Success", () => {5 log.success("Success!". []);6});7test("Error", () => {8 log.error("Error :( ", []);9});10test("Debug", () => {11 log.debug("Debugging...", []);12});13test("Info", () => {14 log.info("Info!", []);15});16test("Warning", () => {17 log.warning("Warning!", []);18});Kullanıcılar ayrıca şu şekilde kritik bir hatayı simüle edebilirler:
1test('Blow everything up', () => {2 log.critical('Boom!')3})Kritik hataları kayıt altına almak, testlerin yürütülmesini durduracak ve her şeyi mahvedecektir. Sonuçta, kodunuzun dağıtımda kritik kayıtları içermediğinden emin olmak istiyoruz ve bunun olması durumunda hemen fark etmeniz gerekiyor.
Türetilmiş alanların test edilmesi
Türetilmiş alanları test etme özelliği, belirli bir varlıkta bir alan belirleyip, bu varlıktan türetilmiş bir alan içeriyoren başka bir varlığın otomatik olarak güncellenmesini sağlayan bir özelliktir.
Before version 0.6.0 it was possible to get the derived entities by accessing them as entity fields/properties, like so:
1let entity = ExampleEntity.load('id')2let derivedEntity = entity.derived_entityAs of version 0.6.0, this is done by using the loadRelated function of graph-node, the derived entities can be accessed the same way as in the handlers.
1test('Derived fields example test', () => {2 let mainAccount = GraphAccount.load('12')!34 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('nameSignalTransactions'))5 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('operatorOf'))67 let operatedAccount = GraphAccount.load('1')!8 operatedAccount.operators = [mainAccount.id]9 operatedAccount.save()1011 mockNameSignalTransaction('1234', mainAccount.id)12 mockNameSignalTransaction('2', mainAccount.id)1314 mainAccount = GraphAccount.load('12')!1516 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('nameSignalTransactions'))17 assert.assertNull(mainAccount.get('operatorOf'))1819 const nameSignalTransactions = mainAccount.nameSignalTransactions.load()20 const operatorsOfMainAccount = mainAccount.operatorOf.load()2122 assert.i32Equals(2, nameSignalTransactions.length)23 assert.i32Equals(1, operatorsOfMainAccount.length)2425 assert.stringEquals('1', operatorsOfMainAccount[0].id)2627 mockNameSignalTransaction('2345', mainAccount.id)2829 let nst = NameSignalTransaction.load('1234')!30 nst.signer = '11'31 nst.save()3233 store.remove('NameSignalTransaction', '2')3435 mainAccount = GraphAccount.load('12')!36 assert.i32Equals(1, mainAccount.nameSignalTransactions.load().length)37})Testing loadInBlock
As of version 0.6.0, users can test loadInBlock by using the mockInBlockStore, it allows mocking entities in the block cache.
1import { afterAll, beforeAll, describe, mockInBlockStore, test } from 'matchstick-as'2import { Gravatar } from '../../generated/schema'34describe('loadInBlock', () => {5 beforeAll(() => {6 mockInBlockStore('Gravatar', 'gravatarId0', gravatar)7 })89 afterAll(() => {10 clearInBlockStore()11 })1213 test('Can use entity.loadInBlock() to retrieve entity from cache store in the current block', () => {14 let retrievedGravatar = Gravatar.loadInBlock('gravatarId0')15 assert.stringEquals('gravatarId0', retrievedGravatar!.get('id')!.toString())16 })1718 test("Returns null when calling entity.loadInBlock() if an entity doesn't exist in the current block", () => {19 let retrievedGravatar = Gravatar.loadInBlock('IDoNotExist')20 assert.assertNull(retrievedGravatar)21 })22})Dinamik Veri Kaynaklarının Test Edilmesi
Testing dynamic data sources can be be done by mocking the return value of the context(), address() and network() functions of the dataSource namespace. These functions currently return the following: context() - returns an empty entity (DataSourceContext), address() - returns 0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000, network() - returns mainnet. The create(...) and createWithContext(...) functions are mocked to do nothing so they don’t need to be called in the tests at all. Changes to the return values can be done through the functions of the dataSourceMock namespace in matchstick-as (version 0.3.0+).
Aşağıdaki örnekte:
Öncelikle aşağıdaki olay işleyicisine sahibiz (veri kaynağı mocklamasını göstermek için kasıtlı olarak amaç değişikliği):
1export function handleApproveTokenDestinations(event: ApproveTokenDestinations): void {2 let tokenLockWallet = TokenLockWallet.load(dataSource.address().toHexString())!3 if (dataSource.network() == 'rinkeby') {4 tokenLockWallet.tokenDestinationsApproved = true5 }6 let context = dataSource.context()7 if (context.get('contextVal')!.toI32() > 0) {8 tokenLockWallet.setBigInt('tokensReleased', BigInt.fromI32(context.get('contextVal')!.toI32()))9 }10 tokenLockWallet.save()11}Ardından, dataSourceMock ad alanındaki yöntemlerden birini kullanarak tüm veri kaynağı fonksiyonları için yeni bir geri dönüş değeri ayarlayan testi görüyoruz:
1import { assert, test, newMockEvent, dataSourceMock } from 'matchstick-as/assembly/index'2import { BigInt, DataSourceContext, Value } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'34import { handleApproveTokenDestinations } from '../../src/token-lock-wallet'5import { ApproveTokenDestinations } from '../../generated/templates/GraphTokenLockWallet/GraphTokenLockWallet'6import { TokenLockWallet } from '../../generated/schema'78test('Data source simple mocking example', () => {9 let addressString = '0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A'10 let address = Address.fromString(addressString)1112 let wallet = new TokenLockWallet(address.toHexString())13 wallet.save()14 let context = new DataSourceContext()15 context.set('contextVal', Value.fromI32(325))16 dataSourceMock.setReturnValues(addressString, 'rinkeby', context)17 let event = changetype<ApproveTokenDestinations>(newMockEvent())1819 assert.assertTrue(!wallet.tokenDestinationsApproved)2021 handleApproveTokenDestinations(event)2223 wallet = TokenLockWallet.load(address.toHexString())!24 assert.assertTrue(wallet.tokenDestinationsApproved)25 assert.bigIntEquals(wallet.tokensReleased, BigInt.fromI32(325))2627 dataSourceMock.resetValues()28})dataSourceMock.resetValues()‘in en sonda çağrıldığına dikkat edin. Bunun nedeni değerler değiştirildiğinde hatırlanır ve varsayılan değerlere geri dönmek istiyorsanız sıfırlanmaları gerekir.
Dinamik veri kaynağı oluşturulmasının test edilmesi
As of version 0.6.0, it is possible to test if a new data source has been created from a template. This feature supports both ethereum/contract and file/ipfs templates. There are four functions for this:
assert.dataSourceCount(templateName, expectedCount)can be used to assert the expected count of data sources from the specified templateassert.dataSourceExists(templateName, address/ipfsHash)asserts that a data source with the specified identifier (could be a contract address or IPFS file hash) from a specified template was createdlogDataSources(templateName)prints all data sources from the specified template to the console for debugging purposesreadFile(path)reads a JSON file that represents an IPFS file and returns the content as Bytes
Testing ethereum/contract templates
1test('ethereum/contract dataSource creation example', () => {2 // Assert there are no dataSources created from GraphTokenLockWallet template3 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 0)45 // Create a new GraphTokenLockWallet datasource with address 0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A6 GraphTokenLockWallet.create(Address.fromString('0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2A'))78 // Assert the dataSource has been created9 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 1)1011 // Add a second dataSource with context12 let context = new DataSourceContext()13 context.set('contextVal', Value.fromI32(325))1415 GraphTokenLockWallet.createWithContext(Address.fromString('0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2B'), context)1617 // Assert there are now 2 dataSources18 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockWallet', 2)1920 // Assert that a dataSource with address "0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2B" was created21 // Keep in mind that `Address` type is transformed to lower case when decoded, so you have to pass the address as all lower case when asserting if it exists22 assert.dataSourceExists('GraphTokenLockWallet', '0xA16081F360e3847006dB660bae1c6d1b2e17eC2B'.toLowerCase())2324 logDataSources('GraphTokenLockWallet')25})Example logDataSource output
1🛠 {2 "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2a": {3 "kind": "ethereum/contract",4 "name": "GraphTokenLockWallet",5 "address": "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2a",6 "context": null7 },8 "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2b": {9 "kind": "ethereum/contract",10 "name": "GraphTokenLockWallet",11 "address": "0xa16081f360e3847006db660bae1c6d1b2e17ec2b",12 "context": {13 "contextVal": {14 "type": "Int",15 "data": 32516 }17 }18 }19}Testing file/ipfs templates
Similarly to contract dynamic data sources, users can test test file data sources and their handlers
Example subgraph.yaml
1...2templates:3 - kind: file/ipfs4 name: GraphTokenLockMetadata5 network: mainnet6 mapping:7 kind: ethereum/events8 apiVersion: 0.0.99 language: wasm/assemblyscript10 file: ./src/token-lock-wallet.ts11 handler: handleMetadata12 entities:13 - TokenLockMetadata14 abis:15 - name: GraphTokenLockWallet16 file: ./abis/GraphTokenLockWallet.jsonExample schema.graphql
1"""2Kilitli GRT tutan Token Kilit Cüzdanları3"""4type TokenLockMetadata @entity {5 "Token kilit cüzdanının adresi"6 id: ID!7 "Serbest bırakma programının başlangıç zamanı"8 startTime: BigInt!9 "Serbest bırakma programının bitiş zamanı"10 endTime: BigInt!11 "Başlangıç zamanı ile bitiş zamanı arasındaki periyot sayısı"12 periods: BigInt!13 "Serbest bırakmaların başladığı zaman"14 releaseStartTime: BigInt!15}Example metadata.json
1{2 "startTime": 1,3 "endTime": 1,4 "periods": 1,5 "releaseStartTime": 16}İşleyici örneği
1export function handleMetadata(content: Bytes): void {2 // dataSource.stringParams() returns the File DataSource CID3 // stringParam() will be mocked in the handler test4 // for more info https://thegraph.com/docs/en/developing/creating-a-subgraph/#create-a-new-handler-to-process-files5 let tokenMetadata = new TokenLockMetadata(dataSource.stringParam())6 const value = json.fromBytes(content).toObject()78 if (value) {9 const startTime = value.get('startTime')10 const endTime = value.get('endTime')11 const periods = value.get('periods')12 const releaseStartTime = value.get('releaseStartTime')1314 if (startTime && endTime && periods && releaseStartTime) {15 tokenMetadata.startTime = startTime.toBigInt()16 tokenMetadata.endTime = endTime.toBigInt()17 tokenMetadata.periods = periods.toBigInt()18 tokenMetadata.releaseStartTime = releaseStartTime.toBigInt()19 }2021 tokenMetadata.save()22 }23}Test örneği
1import { assert, test, dataSourceMock, readFile } from 'matchstick-as'2import { Address, BigInt, Bytes, DataSourceContext, ipfs, json, store, Value } from '@graphprotocol/graph-ts'34import { handleMetadata } from '../../src/token-lock-wallet'5import { TokenLockMetadata } from '../../generated/schema'6import { GraphTokenLockMetadata } from '../../generated/templates'78test('file/ipfs dataSource creation example', () => {9 // Generate the dataSource CID from the ipfsHash + ipfs path file10 // For example QmaXzZhcYnsisuue5WRdQDH6FDvqkLQX1NckLqBYeYYEfm/example.json11 const ipfshash = 'QmaXzZhcYnsisuue5WRdQDH6FDvqkLQX1NckLqBYeYYEfm'12 const CID = `${ipfshash}/example.json`1314 // Create a new dataSource using the generated CID15 GraphTokenLockMetadata.create(CID)1617 // Assert the dataSource has been created18 assert.dataSourceCount('GraphTokenLockMetadata', 1)19 assert.dataSourceExists('GraphTokenLockMetadata', CID)20 logDataSources('GraphTokenLockMetadata')2122 // Now we have to mock the dataSource metadata and specifically dataSource.stringParam()23 // dataSource.stringParams actually uses the value of dataSource.address(), so we will mock the address using dataSourceMock from matchstick-as24 // First we will reset the values and then use dataSourceMock.setAddress() to set the CID25 dataSourceMock.resetValues()26 dataSourceMock.setAddress(CID)2728 // Now we need to generate the Bytes to pass to the dataSource handler29 // For this case we introduced a new function readFile, that reads a local json and returns the content as Bytes30 const content = readFile(`path/to/metadata.json`)31 handleMetadata(content)3233 // Now we will test if a TokenLockMetadata was created34 const metadata = TokenLockMetadata.load(CID)3536 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.endTime, BigInt.fromI32(1))37 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.periods, BigInt.fromI32(1))38 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.releaseStartTime, BigInt.fromI32(1))39 assert.bigIntEquals(metadata!.startTime, BigInt.fromI32(1))40})Test Kapsamı
Using Matchstick, Subgraph developers are able to run a script that will calculate the test coverage of the written unit tests.
The test coverage tool takes the compiled test wasm binaries and converts them to wat files, which can then be easily inspected to see whether or not the handlers defined in subgraph.yaml have been called. Since code coverage (and testing as whole) is in very early stages in AssemblyScript and WebAssembly, Matchstick cannot check for branch coverage. Instead we rely on the assertion that if a given handler has been called, the event/function for it have been properly mocked.
Prerequisites
To run the test coverage functionality provided in Matchstick, there are a few things you need to prepare beforehand:
İşleyicilerinizi dışa aktarın
In order for Matchstick to check which handlers are being run, those handlers need to be exported from the test file. So for instance in our example, in our gravity.test.ts file we have the following handler being imported:
1import { handleNewGravatar } from '../../src/gravity'In order for that function to be visible (for it to be included in the wat file by name) we need to also export it, like this:
1export { handleNewGravatar }Usage
Her şey hazır olduğunda, test kapsama aracını çalıştırmak için basitçe şunu çalıştırın:
1graph test -- -cYou could also add a custom coverage command to your package.json file, like so:
1"scripts": {2 /.../3 "coverage": "graph test -- -c"4 },Bu, kapsama aracını çalıştıracak ve terminalde buna benzer bir şey göreceksiniz:
1$ graph test -c2Skipping download/install step because binary already exists at /Users/petko/work/demo-subgraph/node_modules/binary-install-raw/bin/0.4.034___ ___ _ _ _ _ _5| \/ | | | | | | | (_) | |6| . . | __ _| |_ ___| |__ ___| |_ _ ___| | __7| |\/| |/ _` | __/ __| '_ \/ __| __| |/ __| |/ /8| | | | (_| | || (__| | | \__ \ |_| | (__| <9\_| |_/\__,_|\__\___|_| |_|___/\__|_|\___|_|\_\1011Compiling...1213Running in coverage report mode.14 ️15Reading generated test modules... 🔎️1617Generating coverage report 📝1819Handlers for source 'Gravity':20Handler 'handleNewGravatar' is tested.21Handler 'handleUpdatedGravatar' is not tested.22Handler 'handleCreateGravatar' is tested.23Test coverage: 66.7% (2/3 handlers).2425Handlers for source 'GraphTokenLockWallet':26Handler 'handleTokensReleased' is not tested.27Handler 'handleTokensWithdrawn' is not tested.28Handler 'handleTokensRevoked' is not tested.29Handler 'handleManagerUpdated' is not tested.30Handler 'handleApproveTokenDestinations' is not tested.31Handler 'handleRevokeTokenDestinations' is not tested.32Test coverage: 0.0% (0/6 handlers).3334Global test coverage: 22.2% (2/9 handlers).Tutulan kayıt çıktısında test çalışma süresi
Tutulan kayıt çıktısı test çalışma süresini içerir. İşte buna bir örnek:
[Thu, 31 Mar 2022 13:54:54 +0300] Program executed in: 42.270ms.
Çok rastlanan derleyici hataları
Critical: Could not create WasmInstance from valid module with context: unknown import: wasi_snapshot_preview1::fd_write has not been defined
This means you have used console.log in your code, which is not supported by AssemblyScript. Please consider using the Logging API
ERROR TS2554: Expected ? arguments, but got ?.
return new ethereum.Block(defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddress, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultAddressBytes, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt);
in ~lib/matchstick-as/assembly/defaults.ts(18,12)
ERROR TS2554: Expected ? arguments, but got ?.
return new ethereum.Transaction(defaultAddressBytes, defaultBigInt, defaultAddress, defaultAddress, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultBigInt, defaultAddressBytes, defaultBigInt);
in ~lib/matchstick-as/assembly/defaults.ts(24,12)
The mismatch in arguments is caused by mismatch in graph-ts and matchstick-as. The best way to fix issues like this one is to update everything to the latest released version.
Ek Kaynaklar
For any additional support, check out this demo Subgraph repo using Matchstick.
Geribildirim
Soru, geri bildirim, özellik istekleri veya sadece iletişim kurmak istiyorsanız en iyi yer Matchstick için ayrılmış bir kanal olan 🔥| unit-testing kanalına sahip olduğumuz The Graph Discord’udur.